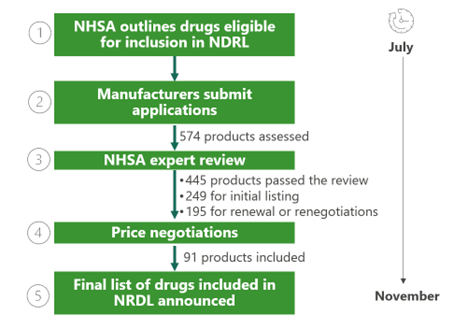
The National Healthcare Security Administration (NHSA) of China completed its annual review of the National Reimbursement Drug List (NDRL) on 28 November. The updated drug catalog will take effect in January 2025. This latest round of updates has taken the total number of medicines on the NRDL to 3,159 (1,765 Western drugs and 1,394 traditional Chinese medicines). The five-step process for review and price negotiation is shown below.1-3
Successful inclusion of a drug in the NRDL depends on multiple factors, including choice of appropriate comparator, clinical value, patient benefit and level of negotiation. A ‘comprehensive group’ of health economic experts and specialists in healthcare evaluates each eligible drug and assigns a score between 1 to 5. This score determines the willingness to pay thresholds, as shown below.

What are the key updates in 2024?
- The NRDL now lists a total of 3,159 medicines (1,765 Western drugs and 1,394 traditional Chinese medicines)
- 91 drugs have been added to the 2025 NRDL, of which 90 have gained market approval within the past five years, and 38 are considered novel drugs worldwide.
- The latest update includes 26 cancer drugs, 15 treatments for diabetes and other chronic diseases, 13 for rare diseases, seven anti-infection medicines and four psychiatric drugs.
- 43 drugs were removed or replaced by more advanced.
How do the latest changes compare with previous NRDL updates?
- Compared to 2013, when China accounted for 3% of all novel drug development pipelines, 2024 China accounted for nearly 28% of novel drug development pipelines worldwide.
- China was the global first-launch market for 29% of new medicines in 2024, compared with just 9% in 2017.
- The average discount rate in 2024 was 63%—the highest level since annual updates to the NRDL began in 2017, but not significantly higher than last year’s discount rate of 61.7%.
- Less than half of those seeking initial listing made it to the shortlist for price negotiation, compared to 64% in 2023 and 67% in 2022.
Most important takeaways
The NRDL remains the principal route for patients in China to access innovative drugs, and it has undergone significant review and refinement since its first introduction in 2018. While a clear preference for domestically developed medicines was observed this year, the choice of comparator (84.6% of reimbursed products with comparators already listed in the NRDL4), the latest round of updates also highlights the increasing level of competition, with more than half of all drugs seeking initial listing failing to be shortlisted for price negotiations5.
Successful inclusion in the NRDL is not sufficient to ensure patient access. Regional budgetary constraints, drug usage, and patient management at the hospital level are essential factors determining patient access. In this context, special arrangements with hospitals, such as agreements on quantities or provision of additional services, must be considered4.
These latest NRDL updates indicate China’s growing prominence as the global first-launch market. This further affirms the growing trend for Chinese companies conducting multi-centre international trials and negotiating several out-licensing deals (e.g., between 2019 and 2023, Chinese manufacturers negotiated around 401 out-licensing deals6).
Source:
- Macabeo B, Wilson L, Xuan J, Guo R, Atanasov P, Zheng L, François C, Laramée P. Access to innovative drugs and the National Reimbursement Drug List in China: Changing dynamics and future trends in pricing and reimbursement. J Mark Access Health Policy. 2023 Jun 13;11(1):2218633.
- Guan, Haijing et al. Impact of competition on reimbursement decisions for cancer drugs in China: an observational study. The Lancet Regional Health – Western Pacific, Volume 50, 101157, 2024
- Yale Jiang, Guo Zhao, Linlin Jia, Cheng Li, Xin Wang, Jing Cai, Huiyao Huang, Shuhang Wang, Ning Li. Trends of drug licensing in China: From bring-in to go-global, Pharmacological Research, Volume 210, 2024